Crafting Feasibility for a Multifamily Real Estate Project
- Manuel (manny ) J.Herrera
- Jul 10, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Aug 25, 2024

The Importance of a Financial Model.
Determining the financial feasibility of a multifamily real estate project from the ground up involves meticulous planning and analysis.
A robust financial model is crucial in this process, serving as a comprehensive tool to evaluate the viability and profitability of the project before the decision to acquire the land is made. Here are some of the reasons why a financial model is essential.
1. Cost Estimation: The model should provide detailed cost estimates for every phase of the project, from land acquisition to construction and operation. It helps identify all potential expenses, including land purchase, site preparation, construction materials, labor, permits, and professional fees.
2. Revenue Projection: By incorporating market analysis data, the model forecasts potential rental income or property sales revenue. This includes considering factors such as rental rates, vacancy rates, and market demand.
3. Risk Assessment: A dynamic financial model allows for scenario analysis, helping developers assess various risks and uncertainties. It can simulate different economic conditions, interest rate changes, and construction delays to understand their impact on the project's profitability.
4. Cash Flow Analysis: The model tracks cash inflows and outflows throughout the project’s lifecycle. This helps ensure that the project maintains positive cash flow and can meet financial obligations at each stage.
5. Financing Needs: By providing a clear picture of the project’s financial requirements, the model aids in determining the amount and type of financing needed. It supports discussions with lenders and investors by demonstrating the project's potential for returns.
6. Investment Evaluation: The model calculates key financial metrics such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and payback period. These metrics are essential for evaluating the project’s attractiveness to investors and stakeholders.
7. Decision Making: With a detailed financial model, developers can make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project. It provides a solid foundation for evaluating the feasibility and aligning the project with financial goals and risk tolerance.
8. Ongoing Monitoring: Once the project is underway, the financial model serves as a tool for ongoing monitoring and management. It helps track actual performance against projections, enabling timely adjustments to keep the project on track.

Summary
In summary, a financial model is indispensable for determining the financial feasibility of a multifamily real estate project. It provides a structured approach to evaluating costs, revenues, risks, and investment potential, ensuring that developers can make informed and strategic decisions from the ground up.
The Financial Model for Land Acquisition

Here's a step-by-step guide to help you set up your Excel sheet for this purpose:
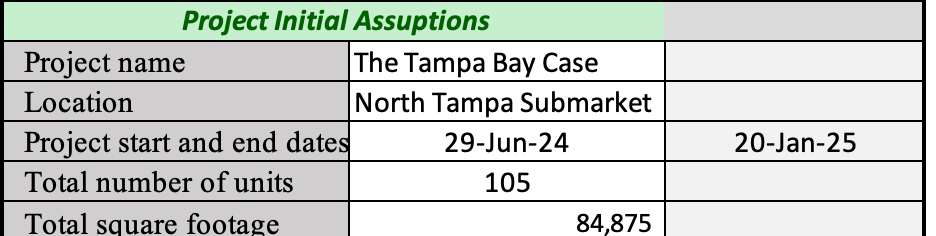
Project Overview
Create a summary tab that includes:
Project name:
Location: Market and Submarket
Project start and end date:
Total number of units:
Total square rentable footage:
Define Unit Mix and Rent amount
Determining the ideal unit mix in a multifamily real estate project involves the consideration of various factors, including market demand, demographic trends, financial considerations, and project goals. A protocol is available for you at Link to assist you in this regard. Our monthly market report, The Multifamily Fundamentals, provides information on the current market and submarket rent by unit type.

Notice the target rent is somewhat lower than the market rent to assume some room for upside.
2. Development Costs.
Create a detailed tab for development costs:
Land Acquisition: Purchase price, and closing costs.
Construction Costs: Costs per square foot.
Soft Costs: Breakdown of architectural, engineering, legal fees, and permits.
Contingency: Typically, a percentage of hard and soft costs.

3. Financial assumptions
Equity: Amount of cash investment.
Debt: Loan amount, interest rate, loan term, maturity.
Loan to Cost Ratio: Calculate the percentage of loan and project cost financing.

The model will produce the monthly payment and the annual service, or the total amount paid at the end of every year.
5. Revenue Projections
Create a revenue projections tab:
Gross Potential Income: Total rentable area times market rent per sqft ($ /square foot per month times 12 months).
Vacancy Allowance: Market Rent Per sqft times rentable area, times 12.
Effective Gross Income: Gross Potential Rent minus Vacancy Allowance. This is the difference between market rent per square foot times rentable space.
Other Income: Laundry, parking, storage fees, etc.
Total Revenue: Effective Gross Income + Other Income.
6. Operating Expenses
Fixed Expenses: Property taxes, insurance
Variable Expenses: Utilities, maintenance, management fees
Total Operating Expenses
7. Net Operating Income (NOI)
NOI=Total Revenue−Total Operating Expenses\text{NOI} = \text{Total Revenue} - \text{Total Operating Expenses}NOI=Total Revenue−Total Operating Expenses.

8. Cash Flow Analysis
Create a cash flow analysis tab:
Debt Service: Annual principal and interest payments
Pre-Tax Cash Flow: NOI - Debt Service

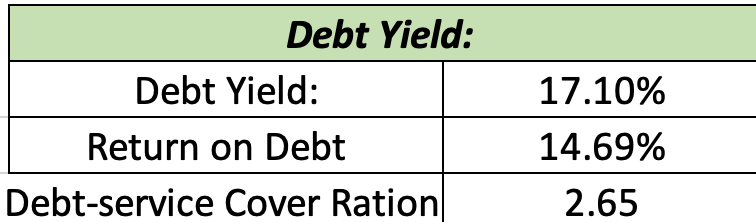
9. Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculate ROI metrics:
Cash on Cash Return: Pre-Tax Cash Flow / Total Equity Investment
Cap Rate: NOI / Total Project Cost
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): Use Excel’s IRR function based on projected cash flows
10. Sensitivity Analysis
Create a sensitivity analysis tab to assess the impact of various assumptions:
By changing rent per unit, vacancy rate, construction costs, Cap Rate, etc you can observe the effect on ROI and feasibility.
Notice:
A complete Financial model is available to supporting members that includes a 5-year financial projection



Comentários